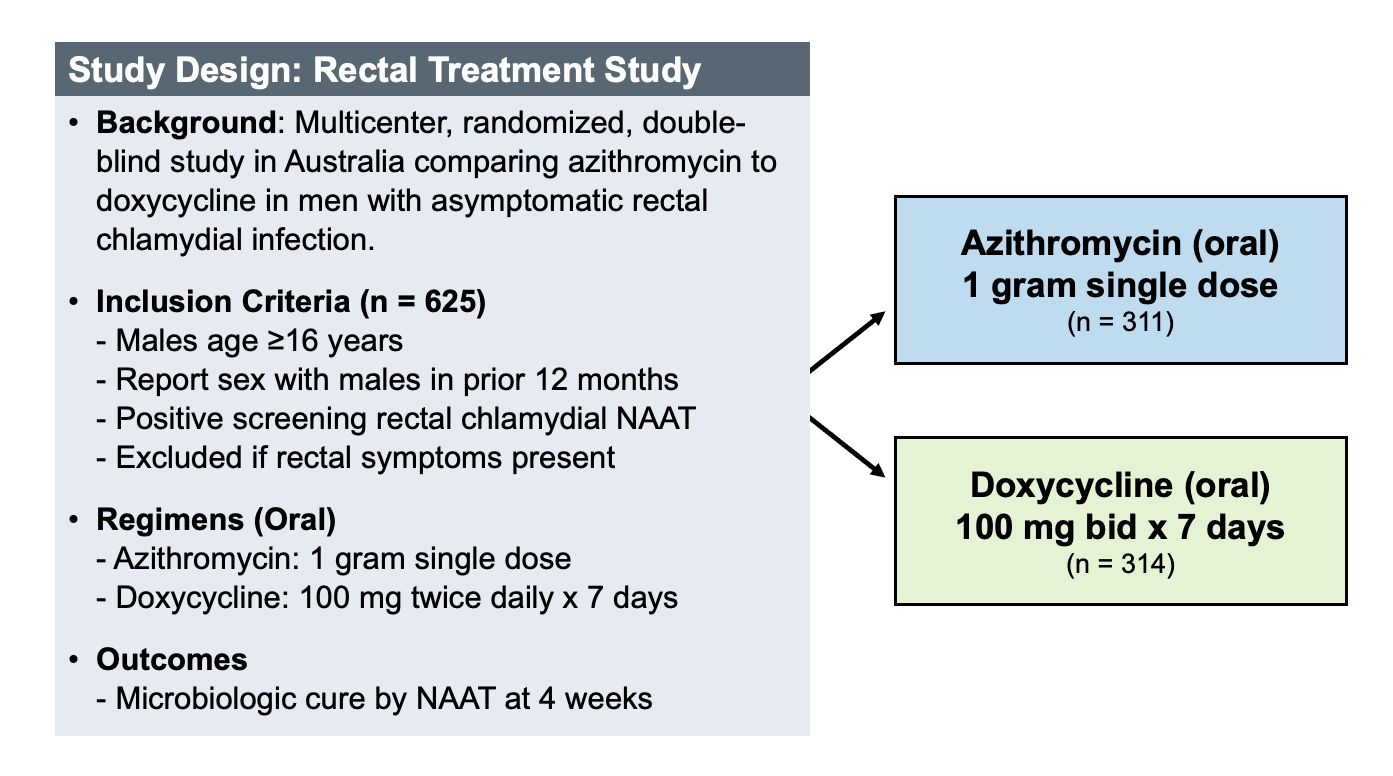
A single 1-gram dose (two 500mg tablets) of azithromycin is a common treatment for chlamydia. This is often administered as a one-time dose, providing a convenient treatment option. However, always consult your doctor for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
While a 1-gram dose is frequently prescribed, alternative regimens exist. Your doctor may recommend a different dosage depending on factors such as your overall health, the severity of your infection, and possible antibiotic resistance. Never self-medicate; accurate diagnosis is critical.
Important Note: Azithromycin is a prescription medication. Obtaining it without a prescription is illegal and potentially harmful. Following your doctor’s instructions precisely is paramount for successful treatment and to minimize potential side effects. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are key to preventing long-term complications.
Potential side effects can include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These are usually mild and temporary. However, seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue.
- Azithromycin 500mg Dosage for Chlamydia: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding the Dosage
- After Treatment
- Potential Side Effects
- Standard Azithromycin Dosage for Chlamydia Treatment
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Medication Interactions
- Who Should Exercise Caution?
- Understanding Your Treatment Plan
- Additional Advice
- Alternatives to Azithromycin for Chlamydia Treatment
- Importance of Partner Notification and Retretesting
Azithromycin 500mg Dosage for Chlamydia: A Detailed Guide
The standard treatment for chlamydia involves a single 1-gram dose (two 500mg tablets) of azithromycin. Take all medication as prescribed by your doctor. This single dose is highly effective, but completing the full course is vital for successful treatment and preventing reinfection or complications.
Understanding the Dosage
Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate dosage based on your specific needs. While a single 1-gram dose is common, they might adjust it depending on factors like your weight, other health conditions, or potential drug interactions. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician. Incorrect dosing can lead to treatment failure.
After Treatment
After taking azithromycin, avoid alcohol and follow any additional instructions given by your healthcare provider. It’s crucial to abstain from sexual activity until your partner(s) have also completed treatment to prevent reinfection. A follow-up appointment is recommended to confirm the treatment’s success through testing.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Less common but more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, require immediate medical attention. Seek medical advice if you experience any unusual symptoms. Azithromycin can interact with other medications, so inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you take.
Standard Azithromycin Dosage for Chlamydia Treatment
The standard single-dose treatment for chlamydia is 1 gram of azithromycin taken orally. This is a one-time dose, meaning you only need to take the medication once.
However, some individuals may require a different treatment regimen. A common alternative is a 7-day course of azithromycin, with 250mg administered once daily. Your doctor will determine the best course of action based on your specific health needs and medical history. Always follow your physician’s prescribed dosage and complete the entire course, even if symptoms improve.
Important Note: Azithromycin is a prescription medication. Do not attempt to self-treat chlamydia. A proper diagnosis and treatment plan from a healthcare provider are crucial for effective treatment and to prevent complications.
Remember to inform your doctor about any other medications you are currently taking, as interactions may occur. Furthermore, discuss potential allergies or sensitivities to antibiotics before starting treatment.
Following your doctor’s instructions carefully will help ensure successful treatment of your chlamydia infection.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Azithromycin, while effective against Chlamydia, can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These usually are mild and resolve without intervention. Less frequent but more serious side effects include allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing), liver problems (jaundice, dark urine), and heart rhythm abnormalities.
Medication Interactions
Azithromycin can interact with certain medications. This includes medications used to treat heart conditions (like digoxin), blood thinners (like warfarin), and some antacids. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking.
Who Should Exercise Caution?
Individuals with pre-existing liver or heart conditions should discuss azithromycin use with their physician before starting treatment. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their doctor as azithromycin can pass into breast milk.
Understanding Your Treatment Plan
| Side Effect | Action |
|---|---|
| Nausea, Diarrhea | Take medication with food. If symptoms worsen, contact your doctor. |
| Allergic Reaction | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Severe Abdominal Pain | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| Jaundice, Dark Urine | Seek immediate medical attention. |
Additional Advice
Complete the entire prescribed course of azithromycin, even if you feel better. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and antibiotic resistance. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. If you have any concerns or questions, contact your healthcare provider. This information is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a physician for diagnosis and treatment.
Alternatives to Azithromycin for Chlamydia Treatment
Doxycycline is a common alternative. Take 100mg twice daily for seven days. This is a reliable and frequently prescribed option.
Another possibility is a single dose of Cefixime, typically 400mg. This is a convenient treatment option, but always follow your doctor’s specific instructions.
For pregnant individuals, erythromycin base is often recommended. The dosage and duration vary depending on the gestational stage; your doctor will provide precise guidance.
Important Note: These are just examples. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting any treatment for Chlamydia. They can assess your specific situation, consider potential interactions with other medications you may be taking, and determine the most appropriate and safe course of action for your health.
They can also discuss potential side effects and ensure appropriate follow-up testing to confirm the infection is cleared.
Importance of Partner Notification and Retretesting
Tell all your recent sexual partners about your Chlamydia infection. This prevents further spread. Contact tracing is key.
- Your doctor or clinic can help you discreetly notify partners, or you can do so yourself.
- Be honest and direct. Explain the importance of testing and treatment to prevent complications.
After completing your Azithromycin course, you must get retested.
- Retesting, typically 3 weeks after treatment, confirms successful eradication of the infection.
- Even if you feel better, retesting is vital. Symptoms can resolve before the infection is completely gone.
- If the test shows persistent infection, alternative treatment options will be discussed.
Consistent condom use with all partners significantly reduces the risk of reinfection and transmission.
- Remember, Chlamydia is easily spread. Protection is vital for your health and the health of your partners.