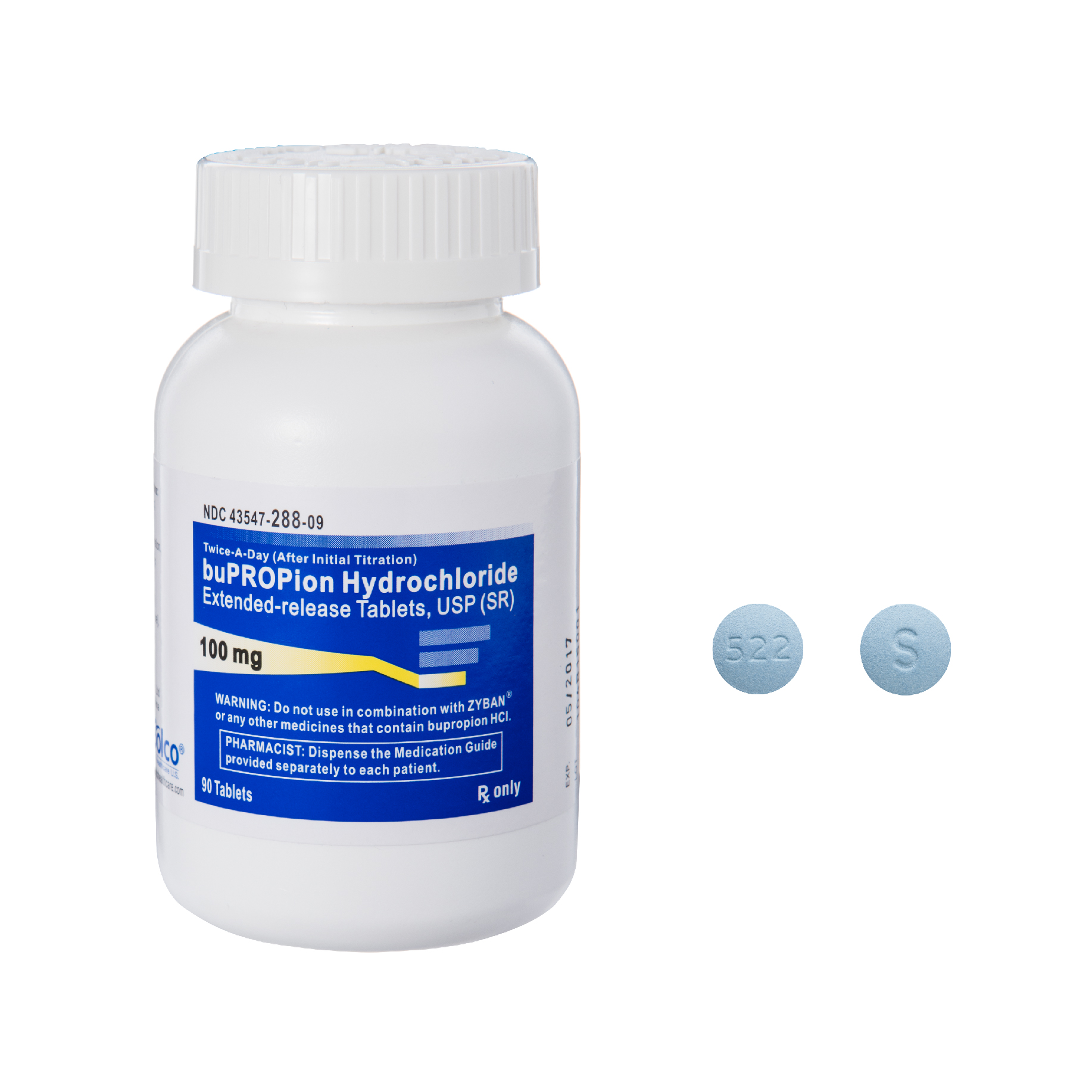
Consider Bupropion if you’re seeking help managing depression or quitting smoking. This medication, available in tablet form, works differently than many other antidepressants, affecting dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain. This unique mechanism can lead to improved mood and reduced cravings.
Always discuss Bupropion with your doctor before starting treatment. They will assess your medical history, current medications, and overall health to determine if it’s the right choice for you. Dosage varies depending on your individual needs and condition, starting generally low and gradually increasing as tolerated. Your physician will create a personalized treatment plan.
Potential side effects include dry mouth, insomnia, headache, and constipation. While generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience more significant reactions. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately. Regular monitoring is part of successful Bupropion therapy, allowing your healthcare professional to adjust the dosage or address any adverse effects promptly.
Remember: Bupropion is not a cure-all, and results can vary. Patience and consistency are key. Your doctor can provide ongoing support and guidance, helping you navigate potential challenges and maximize the benefits of treatment. Active participation in therapy and open communication with your medical team are crucial for optimal results.
- Bupropion Tablets: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is Bupropion and How Does it Work?
- Bupropion’s Uses: Depression, Smoking Cessation, and More
- Available Forms and Dosages of Bupropion Tablets
- Factors Influencing Bupropion Dosage
- Important Considerations
- Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Headache and Dizziness
- Serious Side Effects and When to Seek Medical Attention
- Neurological Effects
- Mental Health Changes
- Allergic Reactions
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- Drug Interactions: What to Avoid When Taking Bupropion
- Alcohol and Bupropion: A Risky Mix
- Other Medications Requiring Caution
- Monitoring and Reporting
- Precautions and Warnings: Who Should Not Take Bupropion?
- Starting and Stopping Bupropion: A Guide for Patients
- Finding Affordable Bupropion: Insurance Coverage and Assistance Programs
- Understanding Your Insurance Plan
- Finding Additional Help
Bupropion Tablets: A Comprehensive Guide
Consult your doctor before starting Bupropion, especially if you have a history of seizures, eating disorders, or are pregnant or breastfeeding. Dosage should be carefully adjusted based on your individual needs and response.
Bupropion comes in various forms, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets. Immediate-release tablets typically require more frequent dosing, while extended-release tablets offer a longer duration of action. Your physician will determine the most appropriate formulation for you.
Common side effects include dry mouth, headache, insomnia, and nausea. These usually lessen over time. However, report any significant or persistent side effects to your doctor immediately. Serious but rare side effects may include seizures and allergic reactions. Seek immediate medical attention if these occur.
Taking Bupropion with alcohol or certain medications can increase the risk of adverse effects. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications and supplements you are taking.
The medication’s effectiveness varies between individuals. Factors like metabolism, underlying conditions, and adherence to the prescribed regimen significantly impact its efficacy. Consistent medication use as directed is key to maximizing its benefits.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Mouth | Common | Drink plenty of water |
| Headache | Common | Over-the-counter pain relievers may help |
| Insomnia | Common | Take medication earlier in the day; discuss with your doctor |
| Nausea | Common | Take with food; discuss with your doctor |
| Seizures | Rare | Seek immediate medical attention |
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are crucial for monitoring your progress and adjusting your treatment plan as needed. This allows for timely intervention if adjustments are necessary.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing any medication.
What is Bupropion and How Does it Work?
Bupropion is an antidepressant medication, also used to aid in smoking cessation. It works differently than many other antidepressants.
Unlike selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), bupropion primarily affects dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain. It does this by blocking their reuptake, increasing their availability in the synaptic cleft.
Increased dopamine is believed to improve mood and motivation, while increased norepinephrine contributes to alertness and focus. This dual mechanism of action is thought to be responsible for bupropion’s effectiveness in treating depression and helping people quit smoking.
It’s important to note that bupropion’s effects on the brain are complex and not fully understood. Research continues to explore its precise mechanism of action. Your doctor can provide specific information regarding your situation.
Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully when taking bupropion. This includes adhering to the prescribed dosage and reporting any side effects promptly.
Bupropion’s Uses: Depression, Smoking Cessation, and More
Bupropion primarily treats major depressive disorder and helps people quit smoking. Doctors frequently prescribe it for adults experiencing depressive symptoms that haven’t responded well to other antidepressants.
For smoking cessation, bupropion reduces nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms, significantly improving quit rates. It’s often used in conjunction with counseling and behavioral therapies for optimal results. Begin using it as directed by your physician.
While less common, bupropion may also be considered for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in certain adults, though other medications are generally preferred. Your doctor will assess your specific needs and determine if it’s appropriate for your condition.
Remember, bupropion is a prescription medication. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any medication, including bupropion, to discuss potential side effects and interactions with other medications. They will help determine the correct dosage and monitor your progress.
Specific side effects vary depending on the individual but can include headache, dry mouth, nausea, insomnia, and constipation. Your doctor will discuss these in detail and help manage any issues that arise.
Available Forms and Dosages of Bupropion Tablets
Bupropion comes in several forms to suit individual needs. You’ll find immediate-release tablets in 75mg, 100mg, and 150mg strengths. These are typically taken multiple times daily. Extended-release tablets offer a 150mg and a 300mg option; these are taken once daily, simplifying the medication schedule. Dosage is determined by your doctor, based on your specific situation and response to treatment.
Factors Influencing Bupropion Dosage
Your doctor considers various aspects when prescribing Bupropion, including your medical history, the specific condition being treated (depression, smoking cessation, or both), and your body’s response to the medication. They’ll carefully monitor your progress and adjust the dose as needed. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and never change your dosage without their guidance. Starting doses are generally lower, gradually increasing as tolerated. Remember, proper adherence to the prescribed dosage is vital for achieving optimal results.
Important Considerations
It’s critical to report any side effects to your physician immediately. They may adjust the dosage or suggest alternative treatments. Never abruptly stop taking Bupropion without consulting your doctor, as this could trigger withdrawal symptoms. Always store the medication safely, away from children and pets.
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Dry mouth is a frequent side effect. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Chewing sugar-free gum can also help.
Insomnia affects some users. Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. If sleep problems persist, talk to your doctor.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Nausea and upset stomach are possible. Take bupropion with food to minimize these effects. Small, frequent meals can also be helpful. If symptoms are severe, consult your physician.
Headache and Dizziness
Headaches and dizziness can occur. Staying hydrated and getting adequate rest are key. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, may provide relief. If headaches are severe or persistent, contact your doctor.
These are just some of the common side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and report any concerning symptoms. Your doctor can adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatment options if necessary.
Serious Side Effects and When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following serious side effects: seizures, severe skin reactions (like Stevens-Johnson syndrome), hallucinations, or thoughts of self-harm or harming others. These are rare but potentially life-threatening.
Neurological Effects
Bupropion can increase the risk of seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of seizures, eating disorders, or head injuries. Report any unusual neurological symptoms such as tremors, muscle twitching, or unusual changes in vision or hearing to your physician without delay.
Mental Health Changes
While bupropion is often used to treat depression, it can also worsen existing mental health conditions or trigger new ones in some individuals. Monitor yourself for heightened anxiety, agitation, unusual irritability, or significant changes in mood. Seek professional help if you experience worsening symptoms or develop new mental health concerns.
Allergic Reactions
Severe allergic reactions, including rash, hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, or tightness in the chest, require immediate medical attention. These reactions are rare but can be dangerous. Stop taking bupropion and seek immediate medical care if you experience any allergic reaction.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Beyond the above serious side effects, contact your doctor if you experience: persistent nausea or vomiting, significant changes in weight, unusual fatigue, rapid heartbeat, or persistent insomnia. Open communication with your doctor is key for safe and effective treatment. Regular monitoring allows for prompt adjustments to your medication regimen as needed.
Drug Interactions: What to Avoid When Taking Bupropion
Avoid combining bupropion with MAO inhibitors. This combination can cause a dangerous increase in blood pressure, potentially leading to serious health complications. Allow at least 14 days between stopping an MAO inhibitor and starting bupropion, and vice versa.
Alcohol and Bupropion: A Risky Mix
Limit or avoid alcohol consumption while taking bupropion. Alcohol can intensify the side effects of bupropion, increasing the risk of dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired judgment. This combination can also negatively impact liver function.
Other Medications Requiring Caution
Caution is advised with certain other medications. Discuss these interactions with your doctor before combining bupropion with: other antidepressants (especially SSRIs and SNRIs), seizure medications, certain blood pressure medications, and drugs that affect the liver. Your doctor can assess potential risks and adjust dosages accordingly. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking.
Monitoring and Reporting
Regularly monitor yourself for any unusual side effects while taking bupropion. Report any new or worsening symptoms promptly to your healthcare provider. Open communication with your healthcare team is key for safe and effective medication management.
Precautions and Warnings: Who Should Not Take Bupropion?
Avoid bupropion if you have a history of seizures or eating disorders. This medication can lower the seizure threshold, increasing your risk of seizures. Similarly, bupropion isn’t suitable for individuals with anorexia or bulimia nervosa.
Individuals currently using or recently discontinued Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) should absolutely avoid bupropion. A dangerous interaction can occur, potentially leading to serious health complications. Allow at least 14 days to elapse between stopping an MAOI and starting bupropion.
If you have severe liver or kidney disease, talk to your doctor before taking bupropion. Your doctor needs to assess your condition and potentially adjust the dosage or find an alternative medication.
Bupropion can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially in younger adults (under 25). Close monitoring is needed, particularly during the initial weeks of treatment. Report any unusual changes in mood or behavior to your doctor immediately.
Always inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Some medications can interact negatively with bupropion.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Discuss bupropion use with your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. The potential risks and benefits need to be carefully weighed.
Driving and operating machinery: Bupropion can cause drowsiness or dizziness in some people. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how the medication affects you.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your physician for personalized guidance before starting or stopping any medication.
Starting and Stopping Bupropion: A Guide for Patients
Your doctor will determine the best starting dose and titration schedule for you. Typically, you’ll begin with a low dose and gradually increase it over several weeks. Closely monitor for side effects and report any concerns immediately.
Starting Bupropion:
- Expect potential side effects like dry mouth, headache, insomnia, and nausea. These are often temporary.
- Drink plenty of water to mitigate dry mouth. Consider taking the medication with food to reduce nausea.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and timing.
- Report any significant side effects to your healthcare provider promptly.
Stopping Bupropion:
Never stop taking Bupropion abruptly. Sudden cessation can cause withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule to gradually reduce your dosage. This usually involves decreasing the dose by a small amount at set intervals.
- Follow your doctor’s prescribed tapering schedule meticulously.
- Anticipate potential withdrawal symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, vivid dreams, or flu-like symptoms. These are usually manageable and temporary.
- Maintain open communication with your doctor throughout the tapering process to address any concerns or adjustments needed.
- If you experience severe withdrawal symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Important Considerations:
- Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking.
- Discuss potential interactions with other drugs, especially those affecting the central nervous system.
- Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Bupropion, as it can increase the risk of side effects.
- Bupropion may affect your ability to drive or operate machinery. Monitor your reaction time and adjust activities as needed.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication.
Finding Affordable Bupropion: Insurance Coverage and Assistance Programs
Check your insurance coverage first. Contact your insurance provider directly to verify Bupropion’s coverage under your plan. Ask about formularies, prior authorizations, and cost-sharing details (copay, coinsurance).
Understanding Your Insurance Plan
- Formulary: This list specifies drugs covered by your plan. Confirm Bupropion is included.
- Prior Authorization: Your doctor might need to obtain pre-approval before your insurance covers Bupropion. Inquire about the process.
- Cost-Sharing: Determine your out-of-pocket expenses – copay, coinsurance, and deductible – for Bupropion.
If your insurance doesn’t cover Bupropion or the cost is prohibitive, explore these options:
- Patient Assistance Programs (PAPs): Many pharmaceutical companies offer PAPs to help individuals afford medications. Check the manufacturer’s website (e.g., GlaxoSmithKline for Bupropion) for details and applications.
- Manufacturer Coupons: Some manufacturers provide coupons or discounts. Search online for Bupropion coupons or visit your pharmacy to inquire.
- Drug Discount Cards: Several companies offer discount cards for prescription medications. Compare cards from various providers to find the best deal for Bupropion at your local pharmacy. Remember to check the terms and conditions.
- Negotiate with your pharmacy: Some pharmacies offer discounts or payment plans. Discuss your financial constraints with the pharmacist.
- Generic Alternatives: If available, a generic version of Bupropion may be significantly cheaper.
Finding Additional Help
For those facing significant financial hardship, consider contacting local health clinics or social service agencies. They might offer assistance or refer you to relevant resources. Also, explore the possibility of telehealth options for more affordable consultations regarding medication management.
Remember to always consult with your doctor before changing medications or dosages.