Prednisolone dosages vary significantly depending on the condition being treated and the patient’s individual characteristics. For example, treating inflammatory bowel disease might require a daily dose of 40-60mg initially, gradually tapering down as the condition improves. This contrasts sharply with allergic reactions, where a much lower dose, perhaps 5-20mg per day, might suffice.
Always follow your doctor’s prescription meticulously. Never adjust your dosage without explicit medical guidance. Incorrect dosage can have serious consequences. Children require significantly lower doses than adults, carefully calculated based on weight and condition. For instance, a child with asthma may receive a dosage of 1-2mg/kg/day, divided into two or more administrations.
Specific conditions necessitate tailored approaches. Rheumatoid arthritis treatment may involve daily doses of 5-15mg, while certain eye conditions might require 1-4mg topically. Always consult your ophthalmologist for topical applications. Remember, these examples are illustrative, not prescriptive. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and medical history.
Monitoring side effects is crucial. Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Report any unusual symptoms to your physician immediately. Careful monitoring and adherence to your physician’s instructions are vital for effective and safe prednisolone therapy.
- Prednisolone Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
- Dosage for Common Conditions
- Dosage Adjustments
- Monitoring and Side Effects
- Determining the Right Prednisolone Dose for Your Condition
- Adjusting Your Dose
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Specific Condition Dosages (Example)
- Remember:
- Prednisolone Dosage Forms and Administration
- Dosage Adjustments
- Important Considerations
- Common Prednisolone Dosage Regimens
- Dosage for Inflammatory Conditions
- Dosage for Allergic Reactions
- Important Considerations
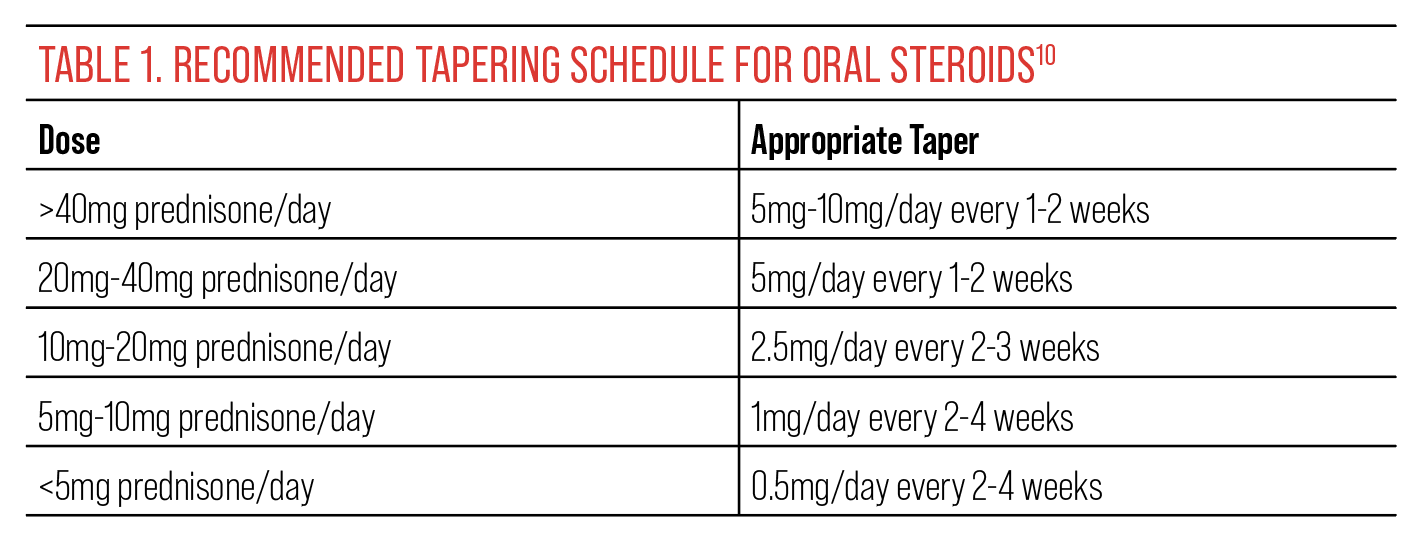
- Tapering Prednisolone
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisolone Dosage
- Dosage Adjustments
- Long-Term Use
- Missed Doses or Unexpected Events
Prednisolone Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
Prednisolone dosage varies significantly depending on the condition being treated, the patient’s age and weight, and their overall health. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions. Never adjust your dosage without consulting them.
Dosage for Common Conditions
For inflammatory conditions like asthma, the initial dose might range from 1 to 2 mg/kg per day, often divided into several smaller doses. This can be gradually reduced as symptoms improve, aiming for the lowest effective dose. For rheumatoid arthritis, dosages vary widely; however, a typical starting range could be 5-60 mg daily, again tapered down over time. In severe cases, higher doses may be necessary initially. Remember: this information is for illustrative purposes only; a physician will determine the correct dosage.
Dosage Adjustments
Doctors often prescribe a tapering schedule when discontinuing prednisolone, gradually lowering the dose to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Rapid cessation can lead to adrenal insufficiency. Factors like age, severity of illness, and patient response influence the tapering speed. A slow, carefully planned reduction is usually recommended. Children require special dosage considerations, with weight being a critical factor in determining the appropriate amount.
Monitoring and Side Effects
Regular monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and potential side effects like weight gain, mood changes, and increased risk of infections is crucial. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. Close collaboration with your healthcare provider is key for safe and effective prednisolone use. This allows for personalized adjustments to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize risks.
Determining the Right Prednisolone Dose for Your Condition
Your doctor determines your Prednisolone dosage based on several factors, primarily your specific condition and its severity. For example, a low dose, perhaps 5-10 mg daily, might suffice for mild allergic reactions. However, more serious conditions like lupus or severe asthma may require significantly higher doses, potentially reaching 60 mg or more daily, initially. This is a starting point; your doctor will carefully monitor your response and adjust accordingly.
Adjusting Your Dose
Dosage adjustments are common. Doctors often begin with a higher dose to achieve rapid symptom control, then gradually taper it down to the lowest effective dose to minimize side effects. This tapering process is crucial and should always be overseen by a physician. Never abruptly stop taking Prednisolone. Rapid reductions can trigger a flare-up of your condition or even adrenal insufficiency.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Your age, weight, and overall health also influence dosage. Children, for example, require lower doses per kilogram of body weight than adults. Concurrent medications can also play a role, as some drugs can interact with Prednisolone. Be sure to inform your doctor about all medications you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor your response to Prednisolone and check for potential side effects.
Specific Condition Dosages (Example)
Note: These are examples only, and your doctor will tailor your dosage to your individual needs. Do not use this information to self-medicate.
Remember:
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding Prednisolone dosage and administration. Open communication with your doctor is key to managing your condition effectively and safely.
Prednisolone Dosage Forms and Administration
Prednisolone comes in several forms: tablets, oral solutions, intravenous solutions, and eye/ear drops. Your doctor will select the most appropriate form based on your specific needs and condition. Oral tablets are common for long-term treatment, while intravenous solutions are used for severe cases requiring immediate action. Eye or ear drops target localized inflammation.
Dosage Adjustments
Dosage depends heavily on the condition being treated and the individual’s response. Doctors often start with a higher dose to achieve rapid symptom control, then gradually reduce the dosage as symptoms improve. This tapering process is vital to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Close monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar, and potassium levels is frequently needed, especially at higher doses. Children require adjusted dosages based on their weight and age. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed schedule carefully. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Important Considerations
Prednisolone can have side effects, including weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, and increased risk of infection. These side effects are generally dose-dependent and often subside with dosage reduction. Regular monitoring by your healthcare provider allows for timely adjustments and management of potential side effects. Inform your doctor about any pre-existing conditions or medications you are taking, as interactions are possible.
Common Prednisolone Dosage Regimens
Prednisolone dosages vary significantly depending on the specific condition being treated and the patient’s individual needs. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Dosage for Inflammatory Conditions
- Asthma: Initial dosages often range from 20-60 mg daily, gradually tapering down as symptoms improve. Maintenance doses are significantly lower.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Starting doses usually fall between 7.5-60 mg daily, adjusted based on response. Long-term use often involves a slow reduction to a minimal effective dose.
- Lupus: Dosages can vary widely, with initial treatments potentially exceeding 60 mg daily before tapering to a maintenance level. Individual responses to treatment will guide dosage adjustments.
Dosage for Allergic Reactions
For severe allergic reactions, higher initial doses–up to 60-100 mg daily–might be used, rapidly decreasing as the reaction subsides. This is usually short-term treatment.
Important Considerations
- Age: Dosages are typically adjusted for children and older adults due to differing metabolic rates and potential side effects.
- Liver and Kidney Function: Impaired liver or kidney function necessitates careful dosage adjustment to prevent drug accumulation.
- Other Medications: Interaction with other drugs needs to be considered, potentially affecting both Prednisolone metabolism and efficacy.
- Patient Response: Dosage adjustments are made based on the patient’s response to treatment. Clinical symptoms, blood tests, and overall well-being will inform the physician’s decisions.
Tapering Prednisolone
Abrupt cessation of Prednisolone can cause severe withdrawal symptoms. Always gradually reduce the dose as directed by your doctor to minimize these risks. A slow reduction is usually preferred over rapid discontinuation.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or changing any medication.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Prednisolone, while effective, carries potential side effects. Managing these requires careful monitoring and adherence to your doctor’s instructions.
Common Side Effects: These often resolve with dosage adjustment or discontinuation. They include:
- Weight gain, primarily due to fluid retention.
- Increased appetite and changes in blood sugar.
- Mood changes, ranging from mild irritability to more serious psychological effects.
- Insomnia or sleep disturbances.
- High blood pressure.
- Acne or skin thinning.
- Muscle weakness.
Less Common, but Serious Side Effects: These require immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing).
- Increased risk of infection due to immune suppression.
- Osteoporosis (weakening of bones), particularly with long-term use.
- Glaucoma or cataracts.
- Gastrointestinal issues, including ulcers and bleeding.
Precautions:
- Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible.
- Report any side effects immediately, no matter how minor they seem.
- Avoid alcohol, as it can exacerbate some side effects.
- Maintain a healthy diet and regular exercise regimen to mitigate potential risks.
- Avoid abrupt discontinuation of prednisolone. Tapering the dose under medical supervision is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar, and bone density may be necessary, depending on your individual circumstances and treatment duration.
- Vaccinations should be discussed with your physician, as prednisolone can affect the immune response.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance on prednisolone use and management of potential side effects.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisolone Dosage
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any severe side effects. These include, but aren’t limited to, severe stomach pain, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, severe mood changes (like extreme anxiety or depression), or vision problems.
Dosage Adjustments
Schedule a doctor’s appointment if you notice your condition isn’t improving as expected, even after taking Prednisolone for several days. Similarly, seek medical advice if your symptoms worsen or new ones appear. Don’t adjust your dosage without consulting your physician; they’ll help determine the best course of action.
Long-Term Use
Regular check-ups are vital if you’re prescribed Prednisolone for a prolonged period. This allows your doctor to monitor potential side effects and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan to minimize risks. Long-term Prednisolone use necessitates close medical supervision. This includes monitoring blood pressure, blood sugar, and bone density.
Missed Doses or Unexpected Events
Always contact your doctor if you miss doses or experience unforeseen circumstances affecting your ability to take Prednisolone as prescribed. They can guide you on the best approach to manage these situations and prevent complications.