Need quick answers about Prednisolone? This steroid medication effectively reduces inflammation, but understanding its usage requires careful attention to detail. We’ll provide you with clear, concise information to help you navigate its effects and potential side effects.
Prednisolone is a corticosteroid prescribed for various inflammatory conditions, including asthma, arthritis, and allergic reactions. Its potency varies depending on the dosage and formulation, so precise adherence to your doctor’s instructions is paramount. Remember, improper usage can lead to serious health consequences.
Potential side effects include increased blood sugar, weight gain, mood swings, and increased susceptibility to infections. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure and glucose levels is crucial during treatment. Discuss any concerns or unusual symptoms with your healthcare provider immediately. They can adjust your dosage or treatment plan as needed.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing your Prednisolone dosage. They can accurately assess your specific needs and create a tailored treatment strategy for optimal results and minimal side effects.
Dosage and Administration: Understanding Prescribed Regimens
Your doctor will determine the correct Prednisolone dose based on your specific condition, age, and weight. Follow their instructions precisely; never adjust the dosage yourself.
Prednisolone comes in various forms: tablets, liquids, and injectable solutions. Oral tablets are typically taken once or twice daily with food to minimize stomach upset. Liquid formulations should be measured accurately using a calibrated measuring device, not a household spoon. Injections are administered by a healthcare professional.
Treatment durations vary widely. Some conditions require short courses (a few days to weeks), while others necessitate longer-term use (months or even years) under close medical supervision. Regular follow-up appointments are critical to monitor your progress and adjust the dosage as needed. Your physician will explain the specific duration and schedule for your treatment.
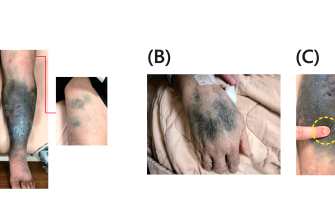
Potential side effects depend on dosage and duration. Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, and difficulty sleeping. Rare but serious side effects exist; immediately report any concerning symptoms to your doctor, such as severe stomach pain, vision problems, or rapid weight gain.
Always inform your doctor of any other medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. This ensures the safest and most effective treatment. Proper storage of your medication is also important. Keep Prednisolone in its original container at room temperature, away from moisture and extreme temperatures.
Remember, this information is for general understanding only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding your Prednisolone prescription.
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Prednisolone can cause various side effects, depending on the dose and duration of treatment. Increased appetite and weight gain are common. To mitigate this, focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables and incorporate regular exercise.
Mood changes, including irritability and anxiety, are also possible. Maintain open communication with your doctor and consider stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga if needed. If severe, discuss alternative medication options with your physician.
High blood sugar levels are a concern, particularly in people with diabetes. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medication accordingly. Maintain a healthy diet and exercise plan to manage blood sugar effectively.
Increased blood pressure is another potential side effect. Regular blood pressure checks are recommended. Dietary changes such as reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium can help control blood pressure.
Osteoporosis is a long-term risk with prolonged use. Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake through diet or supplements. Discuss bone density testing with your doctor.
Fluid retention can lead to swelling in the legs and ankles. Limit salt intake and elevate your legs when resting to help alleviate this.
Insomnia can occur. Establish a regular sleep schedule and avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Your doctor can suggest sleep aids if necessary.
Thinning skin is a potential side effect. Use sunscreen with a high SPF daily to protect your skin from sun damage. Gentle skincare products are advisable.
Always consult your doctor if you experience any concerning side effects. They can help you manage them and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.